Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province and Ministry of Education, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Med-X Research Institute and School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, China
3 Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Aggregation Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Visualizing rapid biological dynamics like neuronal signaling and microvascular flow is crucial yet challenging due to photon noise and motion artifacts. Here we present a deep learning framework for enhancing the spatiotemporal relations of optical microscopy data. Our approach leverages correlations of mirrored perspectives from conjugated scan paths, training a model to suppress noise and motion blur by restoring degraded spatial features. Quantitative validation on vibrational calcium imaging validates significant gains in spatiotemporal correlation (2.2×), signal-to-noise ratio (9–12 dB), structural similarity (6.6×), and motion tolerance compared to raw data. We further apply the framework to diverse in vivo experiments from mouse cerebral hemodynamics to zebrafish cardiac dynamics. This approach enables the clear visualization of the rapid nutrient flow (30 mm/s) in microcirculation and the systolic and diastolic processes of heartbeat (2.7 cycle/s), as well as cellular and vascular structure in deep cortex. Unlike techniques relying on temporal correlations, learning inherent spatial priors avoids motion-induced artifacts. This self-supervised strategy flexibly enhances live microscopy under photon-limited and motion-prone regimes.
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
荧光寿命显微成像(FLIM)已经广泛应用于生命科学研究领域,具有高灵敏和高特异性的特点,在对组织微环境进行定量表征方面具有独特优势,但由于成像速度相对较慢,限制了FLIM的活体应用。近年来,随着光电子器件和人工智能等技术的发展,开启了FLIM活体成像新篇章。介绍通过优化硬件和算法两方面提升时域和频域FLIM技术的成像速度,以及其在生物医学基础研究和临床疾病诊断中的应用研究进展。最后,对活体FLIM成像的未来发展进行展望。
荧光寿命显微成像 人工智能 活体成像 癌症诊断 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(6): 0618005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Key Laboratory for Biomedical Measurements and Ultrasound Imaging, National-Regional Key Technology Engineering Laboratory for Medical Ultrasound, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, US
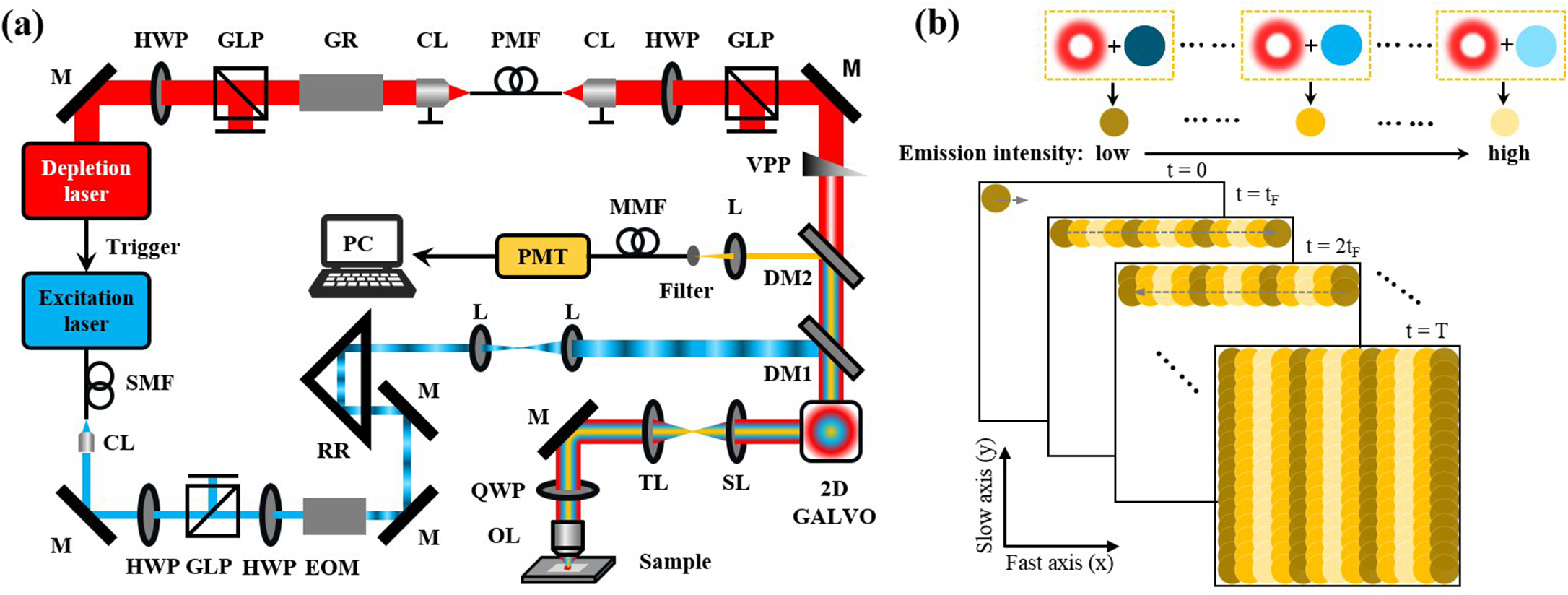
Wide-field linear structured illumination microscopy (LSIM) extends resolution beyond the diffraction limit by moving unresolvable high-frequency information into the passband of the microscopy in the form of moiré fringes. However, due to the diffraction limit, the spatial frequency of the structured illumination pattern cannot be larger than the microscopy cutoff frequency, which results in a twofold resolution improvement over wide-field microscopes. This Letter presents a novel approach in point-scanning LSIM, aimed at achieving higher-resolution improvement by combining stimulated emission depletion (STED) with point-scanning structured illumination microscopy (psSIM) (STED-psSIM). The according structured illumination pattern whose frequency exceeds the microscopy cutoff frequency is produced by scanning the focus of the sinusoidally modulated excitation beam of STED microscopy. The experimental results showed a 1.58-fold resolution improvement over conventional STED microscopy with the same depletion laser power.
stimulated emission depletion structured illumination microscopy superresolution microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031701
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,教育部/广东省光电子器件与系统重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
介绍各种非线性光学显微成像的基本原理,并阐述非线性光学成像的多模态耦合所面临的技术挑战与解决方案。从成像速度、空间分辨率以及信噪比三个方面介绍了多模态非线性光学成像的研究进展,并扩展了多模态非线性光学内窥镜和图像分析方法。最后展望了多模态非线性光学成像的发展趋势和所面临的挑战,以期给相关领域研究人员提供参考。
成像系统 显微成像 非线性光学 多模态光学成像 光学内窥镜
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
高时空分辨可视化技术是脑科学研究的重要工具。荧光显微成像技术在特异性、多样性、图像对比度和时空分辨率等方面具有显著优势,但由于光在组织中的穿透深度有限,无创的荧光成像难以在活体水平获取深层脑区神经血管单元的高分辨结构和功能信息。因此,在脑科学研究中,荧光内窥显微成像技术受到越来越多研究者的青睐。得益于相关科学技术的发展,内窥镜探头在保持高性能的同时,实现了小型化并提供了更大的灵活性,可以植入活体大脑的不同深度处,开展特定深层脑区的功能调控研究。本综述介绍了基于梯度折射率透镜和单根多模光纤这两种探头的植入式荧光内窥显微成像技术及其发展和迭代进程,概述了它们在高分辨活体脑成像研究中的应用,以及在临床神经外科手术中的初步探索性应用。最后,展望了荧光内窥脑成像技术未来的发展前景。
显微 荧光内窥显微成像 活体脑成像 梯度折射率透镜 多模光纤
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Department of Computer Science and Technology, Anhui University of Finance and Economics, Bengbu 233030, China
3 Guangdong-Hongkong-Macau Institute of CNS Regeneration, Ministry of Education CNS Regeneration Collaborative Joint Laboratory, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 Shenzhen Institute of Neuroscience, Shenzhen, 518057, China
5 MOE Frontier Science Center for Brain Science & Brain-Machine Integration, NHC and CAMS Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, School of Brain Science and Brain Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
Visualization of axons and dendritic spines is crucial in neuroscience research. However, traditional microscopy is limited by diffraction-limited resolution and shallow imaging depth, making it difficult to study neuronal dynamics. Two-photon multifocal structured illumination microscopy (2P-MSIM) provides super-resolution imaging along with a reasonably good penetration, but it is vulnerable to optical aberrations in deep tissues. Herein we present a novel non-inertial scanning 2P-MSIM system incorporated with adaptive optics (AO) which allows for super-resolution imaging with effective aberration correction. Our strategy is designed to correct both laser and fluorescence paths simultaneously using a spatial light modulator and a deformable mirror respectively, providing better results than the individual path corrections. The successful implementation of adaptive optical two-photon multifocal structured illumination microscopy (AO 2P-MSIM) has allowed for the super-resolution imaging of neuronal structures in a mouse brain slice at great depths and dynamic morphological characteristics of zebrafish motoneurons in vivo.
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,深圳市光子学与生物光子学重点实验室,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
为进一步提高双光子多焦点结构光照明显微技术(2P-MSIM)的空间分辨率,笔者提出并发展了一种双光子亚衍射多焦点结构光照明显微成像方法(2P-sMSIM)。首先,通过改进的Gerchberg-Saxton(GS)相位恢复算法设计亚衍射聚焦点阵,生成相位图,利用高速相位型空间光调制器产生亚衍射聚焦点阵。通过计算机模拟的仿真实验,探究算法的可行性,并通过对荧光染料溶液的激发成像,证明了每个亚衍射聚焦点阵的平均尺寸为正常衍射受限点阵聚焦点尺寸的80%。其次,将该点阵引入2P-MSIM系统,对固定在BS-C-1细胞内的微管和商用线粒体切片分别进行了超分辨成像实验,证明了在亚衍射聚焦点阵激发下,2P-MSIM的分辨率和成像质量得到了进一步提高,这对于2P-MSIM的发展具有重要意义。
生物光学 多焦点结构光照明显微 亚衍射聚焦点阵 空间光调制器 相位恢复 中国激光
2023, 50(15): 1507103
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong, P. R. China
2 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634 USA
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is suitable for biological samples because of its relatively low-peak illumination intensity requirement and high imaging speed. The system resolution is affected by two typical detection modes: Point detection and area detection. However, a systematic analysis of the imaging performance of the different detection modes of the system has rarely been conducted. In this study, we compared laser point scanning point detection (PS-PD) and point scanning area detection (PS-AD) imaging in nonconfocal microscopy through theoretical analysis and simulated imaging. The results revealed that the imaging resolutions of PS-PD and PS-AD depend on excitation and emission point spread functions (PSFs), respectively. Especially, we combined the second harmonic generation (SHG) of point detection (P-SHG) and area detection (A-SHG) with SIM to realize a nonlinear SIM-imaging technique that improves the imaging resolution. Moreover, we analytically and experimentally compared the nonlinear SIM performance of P-SHG with that of A-SHG.
Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy second harmonic generation Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(4): 2350010
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,射频异质异构集成全国重点研究实验室,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
面向生物粒子操控方法的研究,在生物医学和生命科学等领域具有重要意义。光镊操控具有无接触与高精度的特点,已被广泛应用于多个领域的研究中。然而,传统光镊的光热效应以及衍射极限都制约着光镊在生物医学领域的更广泛应用和发展。近十年来,研究者们将光热效应化劣势为优势,利用光与热的耦合效应实现了多种粒子的精确捕获及操控,即光致温度场光镊(OTFT)。由于此种新型光镊对光能的利用率极高,能量密度低于传统光镊近3个数量级,并可实现颗粒的大范围操控,极大地拓展了光镊可操控粒子的种类,已经成为纳米技术以及生命科学领域的重要研究工具。温度场光镊仍面临诸多问题,例如对于颗粒界面调控的依赖性以及三维捕获受限等,尤其是在生物光子学的研究中,还需要进一步发展和优化。本文对光致温度场光镊操控基本原理及其在生物医学中的应用两个方面进行了系统阐述,并对其今后的发展与挑战进行了展望。
光镊 光热镊 光流控 光热效应 微流控 生物传感器 光学学报
2023, 43(14): 1400001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR, China





